Orthorectification in a Nutshell
Raw satellite imagery contain distortions, which are induced by sensor orientation, topographical variation and the curvature of the earth. When satellite imagery is collected, it needs to be processed to correct for inaccuracies, using a process called orthorectification.
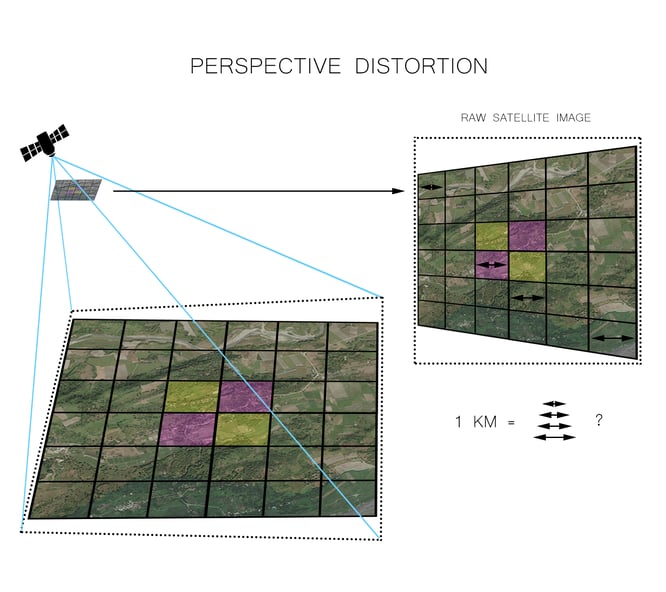
Imagery Distortions
Distortions appear in the form of feature displacement, and create inconsistencies in scaling through the image. Feature displacement of more than 100 meters on sub-meter resolution satellite imagery is not uncommon. The level of distortion changes throughout the imagery scene, which means that a simple ground control point adjustment alone is unable to compensate for these errors. A correction process that considers topographical variations and sensor orientation is required to rearrange the displaced pixels to their correct position. Once orthorectified, the imagery can be used for direct measurement, feature extraction, and other applications requiring measurement-ready data.
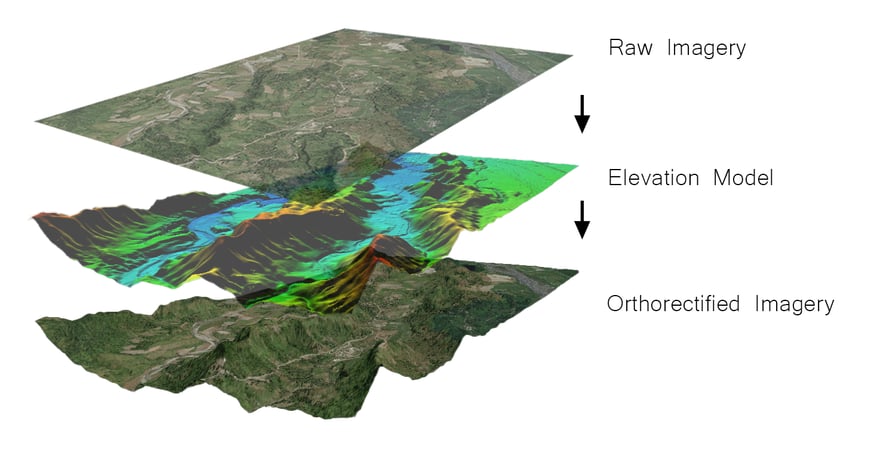
Accurate Elevation Models Are Key
Feature distortion on raw imagery is heavily impacted by terrain variation. An accurate elevation model is required to calculate the effect of terrain variation on the image pixels. This calculation can then be used to accurately position the pixels to the correct locations. Although there are free terrain data sources available, such as SRTM and ASTER, the low level of detail and accuracy result in poorly rectified imagery. If you use 30m SRTM to correct 5m imagery, there is not enough terrain detail to accurately reposition the image pixels. Therefore, it is important to use terrain data that has high resolution and accuracy.
The importance of using accurate elevation models for orthorectification is often overlooked. The most common reasons are due to the cost of procuring accurate elevation data, poor coverage of data in the geographic area of interest, and inconsistent quality and specification. Additionally, performing your own orthorectification means investing in software, hardware, data, and skilled personnel. However, these are not reasons to overlook higher quality elevation models, because if you are relying heavily on satellite imagery in your practice, you need that imagery to be as detailed and reliable as possible.
The next article will highlight some of the key differences between resolution and accuracy, when it comes to satellite imagery.
We at Intermap Technologies® are passionate about geospatial technology and applications. We work with numerous industries and process data to provide location-based answers. This blog series will highlight how geospatial data processing plays an important role in imagery applications.



COMMENTS